Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an increasingly popular choice for businesses. According to Gartner, by 2023, 60% of large and global enterprises, along with 80% of small and mid-sized organizations, will adopt MFA to bolster their account security.
When you log into your online accounts, a process called “authentication,” you’re essentially proving your identity to the service. Traditionally, this involved using a username and password, but this method isn’t foolproof. Usernames can be easily discovered, and people often opt for simple passwords or use the same one across multiple sites due to memory constraints.
Corporate accounts house valuable company data and personal information, demanding protection from potential threats. Consequently, many businesses are turning to identity management platforms to enforce multi-factor authentication across their corporate applications.
In this article, we will understand multi-factor authentication, exploring its crucial role in securing company accounts. We’ll break down how MFA operates and guide businesses through the deployment of MFA.
Table of contents
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) stands as a multi-step protocol for logging into an account, requiring users to input more than just a password. In this process, users may, for instance, need to provide a code sent to their email, respond to a secret question, or utilize fingerprint scanning. This additional layer of authentication serves as a safeguard against unauthorized access, especially in cases where a system password may have been compromised.
Why is it Important?
The necessity for multi-factor authentication arises from the paramount importance of digital security in our contemporary landscape. In a world where businesses and individuals store sensitive information online, the prevalence of online accounts poses a risk of serious consequences, including financial theft, business disruption, and the compromise of privacy.
While passwords offer a basic level of protection, they fall short in the face of determined cybercriminals actively seeking to uncover them. A single discovered password could potentially grant access to multiple accounts if reused. Multi-factor authentication functions as an extra shield, thwarting unauthorized access even when a password has been pilfered. Businesses utilize MFA to verify user identities, ensuring secure and efficient access for authorized users.
Benefits
Here are some benefits of multi-factor authentication:
Risk Reduction
Multi-factor authentication acts as a safeguard. It reduces security risks stemming from human errors, like forgotten passwords or misplaced devices.
Facilitating Digital Initiatives
Organizations can confidently embark on digital initiatives, utilizing multi-factor authentication to secure organizational and user data, ensuring secure online interactions and transactions.
Enhanced Security Response
Customizable multi-factor authentication systems can actively alert stakeholders to suspicious login attempts. It enables swift responses to cyber threats, minimizing potential damage.
Role of Multi-Factor Authentication in Business
The adoption of cloud applications has undergone a revolutionary transformation. Businesses now heavily rely on these applications for their advanced features, increased productivity, and collaboration within virtual teams. This reliance has become even more vital, especially during the Covid-19 pandemic, where remote collaboration is indispensable for ongoing business success.
As organizations increasingly depend on these accounts, ensuring their security becomes paramount. According to Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, stolen credentials and account compromises are identified as the primary causes of data breaches in organizations. This underscores the major role of multi-factor authentication in fortifying the security landscape of business operations.
Types
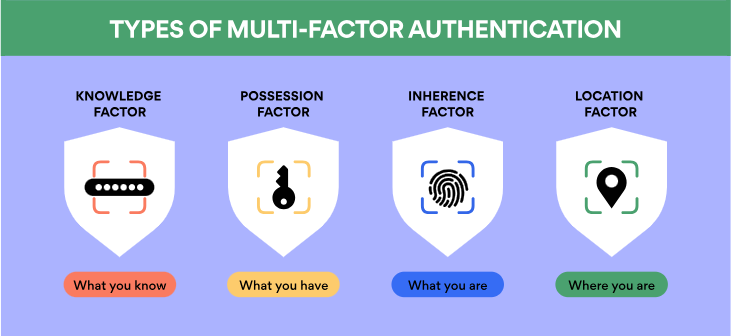
MFA authentication methods typically fall into one of three categories, each relying on different types of additional information:
Knowledge-Based
- Password or PIN
- Involves information you know, enhancing security through what you remember

Possession-Based
- Badge or smartphone
- Requires something you have, adding a layer of security through physical possession
Inherence-Based
- Biometrics like fingerprints or voice recognition
- Utilizes inherent characteristics, such as biometrics, for authentication, adding a unique and personal dimension to security
How Does It Work?
Multi-factor authentication operates by incorporating a multi-step process during account creation. Users submit various forms of identification, which are stored by the system for future logins. The login procedure encompasses multiple stages, necessitating the confirmation of additional identification details along with the password.
Here’s a breakdown of the multi-factor authentication process:
Account Setup
Users establish an account using a username and password, and they also link other elements like a mobile device or a physical hardware fob. These could also be virtual, such as an email address, mobile number, or authenticator app code. Maintaining the confidentiality of these elements is crucial for user identification.
User Verification
When an MFA-enabled user logs into a website, they input their username and password (the first factor – knowledge) and provide an authentication response from their MFA device (the second factor – possession). If the password is confirmed, the system engages with the linked items. For instance, it might generate a numerical code for the hardware device or send a code via SMS to the user’s mobile device.
Final Confirmation
The user completes the authentication by validating the details of the linked items. This could involve entering a code or activating a button on the hardware device. Access to the system is granted only upon the successful verification of all provided information.
How To Install?
To install multi-factor authentication (MFA) on your devices, follow these steps:
- Select a mobile app compliant with RFC 6238, supporting the time-based one-time password (TOTP) algorithm. These apps generate a six-digit authentication code.
- Download and install the selected virtual MFA app on your smartphone or other device.
- Access the AWS Management Console and navigate to the IAM console at https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/iam/home
- Under the Security Credentials tab, choose “Assign MFA device” for the desired IAM user.
- In the setup wizard, enter a device name, choose “Authenticator app,” and proceed. The wizard provides configuration details and a QR code.
- Open your virtual MFA app and either scan the QR code or manually enter the secret key provided by the wizard.
- Once configured, the virtual MFA device starts generating one-time passwords. Enter the displayed codes into the MFA setup wizard within 30 seconds.
- Submit your request immediately after generating the codes to avoid synchronization issues. The virtual MFA device is now ready for use with AWS.
- If needed, the virtual MFA app allows for the creation of multiple devices. It is useful for managing multiple AWS accounts or users.
Implementation
The implementation of multi-factor authentication can take various forms, and here are some examples:
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
The system requests the password along with one additional form of identification, constituting a two-factor or two-step authentication process.
Third-Party Authenticator Application
Instead of the system, a third-party application, known as an authenticator, verifies the user’s identity. The user inputs a passcode into the authenticator, which then confirms the user with the system.
Biometric Verification
During the verification process, the user provides biometric information by scanning a fingerprint, retina, or another body part, enhancing security through unique physical characteristics.
Device Recognition
The system may require multiple authentications only during initial access on a new device. Subsequently, it recognizes the device, asking only for the password for subsequent logins.
These diverse approaches showcase the flexibility of implementing multi-factor authentication to enhance security measures.
Adaptive Authentication
Adaptive authentication represents an intelligent approach to implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA). With each login attempt, adaptive authentication systems assess various contextual factors to conduct a risk evaluation.
Typically, the system scrutinizes factors like location, device used for login, time of day, and network connection. These factors are compared against established patterns of normal account log-ins to determine the risk level of the current attempt.
If the login is deemed safe, the user gains access with a single authentication factor. Conversely, if the attempt is identified as risky, the user is prompted to undergo additional verification steps to ensure account security.
In practical scenarios, a routine login from a familiar work device might be swiftly approved, recognizing it as safe. On the other hand, if a login attempt originates from a compromised device in a foreign location while the user is inactive, the adaptive authentication system triggers additional verification steps due to the perceived risk.
This approach ensures that everyday users can access their corporate accounts easily in most cases, without the need for multiple authentication methods every time. Simultaneously, it maintains a high level of account security by prompting additional verification steps when a potentially risky login is detected.
What Should One Look For?
When considering the implementation of a multi-factor authentication solution for your organization, several crucial features warrant attention during the evaluation and comparison process:
Secure and Versatile Authentication
Go for solutions supporting adaptive authentication and single sign-on, balancing user convenience with robust account security. Ensure compatibility with various authentication methods, such as SMS passcodes, OTPs, biometrics, and physical tokens, for comprehensive user accessibility.
Cloud-Based with Simple User Provisioning
Seek cloud-based solutions that eliminate the need for on-premise setup or additional hardware. This not only reduces costs but also streamlines administrative tasks. Look for solutions offering easy user onboarding through features like Active Directory sync and user self-enrollment.
Simple Integrations
Prioritize solutions that seamlessly integrate with existing accounts and applications through API-based connections. Verify the range of supported applications and consider solutions that accommodate on-premise and custom-built applications for comprehensive coverage.
Admin Dashboard
Choose solutions equipped with a comprehensive admin dashboard, empowering administrators to manage user authentication policies, access reports on login attempts, and monitor security incidents. Additionally, ensure easy user deprovisioning capabilities to promptly revoke access for departed employees.
Free Trial Option
Choose solutions that offer a free trial, allowing your organization to assess the service’s effectiveness across a representative user sample. This trial period enables you to gauge the solution’s alignment with your broader security objectives before committing to its implementation.
In a world where keeping our digital information safe is crucial, adopting multi-factor authentication helps add an extra lock to your online doors. Now, whether it’s your work account or personal email, you’ve got an extra layer of protection standing guard.
